11th Physics MCQs Preparation 2022 and Onwards (Unit: Force and Motion: Set-1 (34 MCQs)) for National MDCAT, ECAT, FPSC, PPSC, JOB Exam, Physics Lecturer, SSC, HSSC (F.Sc.), BS, MS Exams NTS, ETS, etc.
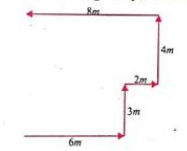
The shortest distance is called displacement. 4m + 3m = 7m
2. Acceleration due to the uniform velocity of a body is
If a body is moving with uniform velocity, the acceleration will be zero in the direction of motion.
3. Third equation of motion is independent of:
2aS= vf² - vi²
S = 80-20 = 60 m and t = 4 hrs - 2 hrs = 2, so, v = `\frac {s}{t}` = v = `\frac {60 m}{2 h}` = 30 km h⁻¹
5. What will be the velocity of a body when it starts its motion from rest and after 5s its acceleration becomes 2 m s⁻¹
vi = 0 m s⁻¹, a = 2 m s⁻¹, t = 5s, Now using 1st equation of motion vf = vi + at = 0 + 2 x 5 = 10 m s⁻¹
Velocity = displacement / time `\vec v` = `\frac {vec v}{t}` Here displacemennt is two radius ie 2 x 2m = 4m and t= 2s so, `\vec v` = `\frac {4m}{2s}`= 2 m s⁻¹
vi = 0 m s⁻¹, a = 2 m s⁻¹, t = 5s, Now using 1st equation of motion vf = vi + at = 0 + 2 x 5 = 10 m s⁻¹
6. What is the velocity of an object when it reaches point P to point Q in 2s along a semicircle radius 2m?
Velocity = displacement / time `\vec v` = `\frac {vec v}{t}` Here displacemennt is two radius ie 2 x 2m = 4m and t= 2s so, `\vec v` = `\frac {4m}{2s}`= 2 m s⁻¹
7. The Sl unit of weight is :
Wieght is force
8. What is the acceleration produced by a force of 0.5 N applied on a body of mass 0.1 kg?
F= ma or a = `\frac {F}{m}` = `\frac {0.5 N}{0.1 kg}` = 5 m s⁻²
9. Three masses that are connected by a massless spring are shown in the figure. What will be the value of F₂ ?
⇒ F₁ = 5a kg -----------(1) where a is the acceleration ⇒ F₂ - F₁ = 3a kg --------(2) ⇒ 30 N - F₂ = 2a kg --------(3) ⇒ by adding (1) and (2) we get F₂ = 8a kg ------------(4) ⇒ by adding (3) and (4) we get 30 N = 10 a kg or a = 3 m s⁻² ⇒ putting the value of a in equation (4) F₂ = 8 (3 m s⁻²) kg = 24 N
10. Rate of change of momentum is
F = ma = m `\frac{v}{t}` =`\frac{mv}{t}` = `\frac{ΔP}{Δt}`
11. A body moves from point P to Q with a speed of 6 m s⁻¹ along a straight line then from Q to P with a speed of 4 m s⁻¹. What is the average speed over the entire trip?
Average Speed = `\frac {v_1 + v_2}{2}`
Impulse = ΔF x Δt
13. Impulse always changed
Impulse-Momentum Theorem
----------------------------
As the horizontal component of the velocity remain constant in projectile motion, so ax = 0
Formula for Height of Projectile H = `\frac {(v_0 sinፀ)^2 }{2g}` so, if ፀ = 90° and Sine 90° =1 so maximum height
--------------------------
Compare the equation of Range and height of the projectile and we will get 0 = tan⁻¹ (4) = 76°
------------------------
---------------------
The maximum range of the projectile is 45°
-------------------
T = v₀ sinθ / g = 100 m s⁻¹ sin (90°)/10 m s⁻² = 10 s
---------------------
Impulse-Momentum Theorem
14. In a one-dimensional elastic collision of two bodies of the same masses, what will happen if the moving body collides with the mass which is initially at rest?
----------------------------
15. In projectile motion, the horizontal component of acceleration of a body is:
As the horizontal component of the velocity remain constant in projectile motion, so ax = 0
16.. At what angle a projectile gain its maximum height:
Formula for Height of Projectile H = `\frac {(v_0 sinፀ)^2 }{2g}` so, if ፀ = 90° and Sine 90° =1 so maximum height
17. A rocket works on basis of :
--------------------------
18. The vertical and horizontal distances of the projectile will be equal if the angle of projection is:
Compare the equation of Range and height of the projectile and we will get 0 = tan⁻¹ (4) = 76°
19. The quantitative measure of the inertia of a body is:
------------------------
20. Range of a projectile on a horizontal plane is the same for the following pair of angles:
---------------------
21. To improve the jumping record the long jumper should jump at an angle of
The maximum range of the projectile is 45°
22. A projectile is launched at 45° to the horizontal with an initial kinetic energy of E. Assuming air resistance to be negligible what will be the kinetic energy of the projectile when it reaches its highest point?
-------------------
23. A projectile is thrown horizontally from a 490m high cliff with a velocity of 100 m s⁻¹. The time taken by the projectile to reach the ground is
T = v₀ sinθ / g = 100 m s⁻¹ sin (90°)/10 m s⁻² = 10 s
24. During projectile motion, the horizontal component of velocity:
---------------------
25. A body is traveling with a constant acceleration of 10 m s⁻². If S₁ is the distance traveled in 1st second and S₂ is the distance traveled in 2nd second, which of the following shows a correct relation between S₁ and S₂?
Assuming the body is starting from rest i.e. vi = 0 m/s and a=10m/s^2, using 2nd equation of motion S = vit + (1/2) at² ---- For t = 1 s S₁ = 0 + (1/2)10 t^2=5(1)^2 = 5 m for t = 2 s, S₂ = 0 + (1/2)10(2)^2 = 20 m So, S₂ = 20 - S₁ = 20 m - 5 m = 15 m = 3 x 5 m = 3 S₁
Initial momentum = Final Momentum = + 4 N s
J = F x Δt
F = ma or a= F/m = 5 N/7 kg= 0.71 m/s²
Negative Acceleration is also called Deceleration or Retardation
--------------------
Assuming the body is starting from rest i.e. vi = 0 m/s and a=10m/s^2, using 2nd equation of motion S = vit + (1/2) at² ---- For t = 1 s S₁ = 0 + (1/2)10 t^2=5(1)^2 = 5 m for t = 2 s, S₂ = 0 + (1/2)10(2)^2 = 20 m So, S₂ = 20 - S₁ = 20 m - 5 m = 15 m = 3 x 5 m = 3 S₁
26. A ball with original momentum +4.0 kg m/s hits a wall and bounces straight back without losing any kinetic energy. The change in momentum of the ball is:
Initial momentum = Final Momentum = + 4 N s
27. SI unit of impulse is: :
J = F x Δt
28. A 7.0 kg bowling ball experiences a net force of 5.0 N. What will be its acceleration?
F = ma or a= F/m = 5 N/7 kg= 0.71 m/s²
29. If the slope of the velocity-time graph gradually decreases, then the body is said to be moving with:
Negative Acceleration is also called Deceleration or Retardation
30. The area between the velocity-time graph is numerically equal to:
--------------------
31. The time rate of change of momentum gives
F = Δp/Δt
While throwing the ball down its velocity depends on the force with which it is thrown ( ie. by applying a greater force greater will be the velocity) but its acceleration is the same as in the free fall motion is 9.8 m/s².
Average velocity = total displacement / total time --- by using Vf = Vi + at to calculate t. (vi = 19.6 m/s (given), vf = 0 m/s (at highest point), and g = - 9.81 m/s² (-ve due to upward motion), we get t = 2 s, so total time of flight will = 2 s (upwards) + 2 s (downwards) = 4 s ---- Now using s = vi t + (1/2) at² we will get the upwards motion distance s = 19.6 m, thus the total distance of the trip is =19.6 m (upwards) + 19.6 m (downwards) = 39.2 m, so Average velocity = 39.2 / 4 = 9.8 m/s. Thus Correct answer is option B.
F = Δp/Δt
32. If you throw a ball downward, then its acceleration immediately after leaving your hand, assuming no air resistance, is
While throwing the ball down its velocity depends on the force with which it is thrown ( ie. by applying a greater force greater will be the velocity) but its acceleration is the same as in the free fall motion is 9.8 m/s².
33. A ball is thrown vertically upwards at 19.6 m/s. For its complete trip (up and back down to the starting position), its average speed is:
Average velocity = total displacement / total time --- by using Vf = Vi + at to calculate t. (vi = 19.6 m/s (given), vf = 0 m/s (at highest point), and g = - 9.81 m/s² (-ve due to upward motion), we get t = 2 s, so total time of flight will = 2 s (upwards) + 2 s (downwards) = 4 s ---- Now using s = vi t + (1/2) at² we will get the upwards motion distance s = 19.6 m, thus the total distance of the trip is =19.6 m (upwards) + 19.6 m (downwards) = 39.2 m, so Average velocity = 39.2 / 4 = 9.8 m/s. Thus Correct answer is option B.
************************************
Or